一、CSS 1.1 基础知识 盒子模型 定义
CSS 基础框盒模型是 CSS 规范的一个模块,它定义了一种长方形的盒子, 包括它们各自的内边距(padding)与外边距(margin ),并根据视觉格式化模型来生成元素,对其进行布置、编排、布局(lay out)。常被直译为盒子模型、盒模型或框模型
分类
盒模型从标准定义上分为标准盒模型和替代(IE)盒模型
标准盒模型的宽高计算方式:width = width; height = height
替代(IE)盒模型的宽高计算方式:width = width + padding + border; height = height + padding + border
盒模型切换
标准盒模型 box-sizing: content-box,默认情况
替代(IE)盒模型 box-sizing:border-box
从元素类型上分为块级盒子(Block box) 和 内联盒子(Inline box)
BFC 定义
块格式化上下文(Block FormattingContext,BFC) 是 Web 页面的可视 CSS 渲染的一部分,是块盒子的布局过程发生的区域,也是浮动元素与其他元素交互的区域。 简单的说BFC是一个完全独立的空间, 这个空间里子元素的渲染不会影响到外面的布局
创建BFC
常见:
完整:
根元素()
浮动元素(元素的 float 不是 none)
绝对定位元素(元素的 position为 absolute 或 fixed)
行内块元素(元素的 display为 inline-block)
表格单元格(元素的 display为 table-cell,HTML表格单元格默认为该值)
表格标题(元素的 display为 table-caption,HTML表格标题默认为该值)
匿名表格单元格元素(元素的 display为 table、table-row、 table-row-group、table-header-group、table-footer-group(分别是HTML table、row、tbody、thead、tfoot 的默认属性)或 inline-table)
overflow 计算值(Computed)不为 visible 的块元素
display值为 flow-root 的元素
contain值为 layout、content 或 paint 的元素
弹性元素(display为 flex或 inline-flex元素的直接子元素)
网格元素(display为 grid 或 inline-grid 元素的直接子元素)
多列容器(元素的 column-count 或 column-width (en-US) 不为 auto,包括 column-count 为 1)
column-span为 all的元素始终会创建一个新的BFC,即使该元素没有包裹在一个多列容器中(标准变更,Chrome bug)。
css 选择器 1.2 面试题 什么是盒模型? 盒模型的分类有? 盒模型的切换? 什么是 BFC? 如何创建 BFC? BFC 解决的什么问题?
使用Float脱离文档流,父元素高度塌陷问题
垂直方向margin重叠的问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" /> <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title > css-box</title > <style > .test { background: red; color: black; width: 200px; line-height: 100px; text-align: center; margin: 50px; } .box-container { overflow: hidden; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="test" > box-one</div > <div class ="test" > box-two</div > <div class ="test" > box-one</div > <div class ="box-container" > <div class ="test" > box-two</div > </div > </body > </html >
什么是 css 选择器优先级
css选择器优先级是基于不同种类选择器组成的匹配规则
css 选择器的优先级
!important> 行内样式 > ID 选择器 > 类、伪类、属性选择器> 标签、伪元素选择器> 通配符、子类选择器、兄弟选择器
CSS 选择器是什么?
通俗的讲 CSS 选择器 用来对选定的页面元素进行样式修改
css 选择器有哪些? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 选择器 式例 标签选择器 h1 { } 通配选择器 * { } 类选择器 .box { } ID 选择器 #unique { } 标签属性选择器 a[title] { } 伪类选择器 p:first-child { } 伪元素选择器 p::first-line { } 后代选择器 article p 子代选择器 article > p 相邻兄弟选择器 h1 + p 通用兄弟选择器 h1 ~ p
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 a [title] {color : purple;} a [href="https://example.org" ] {color : green;} a [href*='example' ] {font-size : 2em ;} a [href$='.org' ] {font-style : italic;} a [class~='logo' ] {padding : 2px ;}
伪元素选择器
伪元素是一个附加至选择器末的关键词,允许你对被选择元素的特定部分修改样式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" /> <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title > Document</title > <style > p { width: 60px; } p ::first-line { color: blue; text-transform: uppercase; } </style > </head > <body > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > <p > 程序员的梦工厂 </p > </body > </html >
通 用 兄 弟 选 择 器
位 置 无 须 紧 邻,只 须 同 层 级,A~ B 选 择 A 元 素 之 后 所 有 同 层 级 B 元 素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" /> <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" /> <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> <title > Document</title > <style > p~span { color: red; } </style > </head > <body > <span > This is not red.</span > <p > Here is a paragraph.</p > <code > Here is some code.</code > <span > This is red</span > <span > This is red</span > </body > </html >
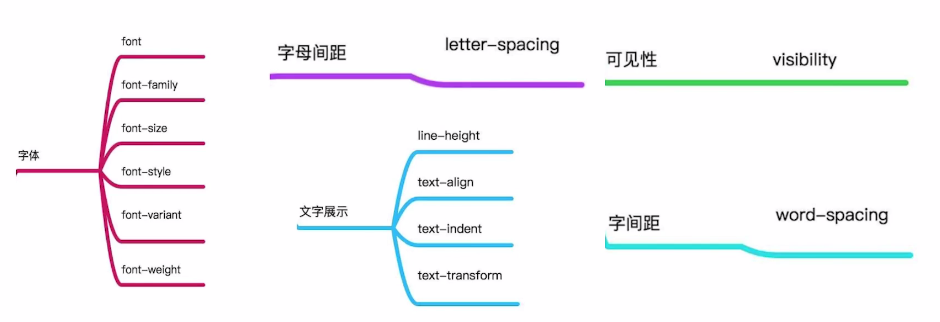
CSS中哪些属性是可以继承的?
px、em、rem、vw+vh区别 px: 绝对单位,网页开发基本长度单位 1px = 2像素
三栏布局 float 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > CSS实现三栏布局-浮动布局</title > <style type ="text/css" > * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } div { height: 100px; } .left { float: left; width: 100px; background: red; } .center { background: green; margin-left: 100px; margin-right: 100px; } .right { float: right; width: 100px; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box" > <div class ="left" > left</div > <div class ="right" > right</div > <div class ="center" > center</div > </div > </body > </html >
flex 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > CSS实现三栏布局-flex布局</title > <style type ="text/css" > * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { display: flex; } div { height: 100px; } .left { width: 100px; background: red; } .center { flex: 1; background: green; } .right { width: 100px; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box" > <div class ="left" > left</div > <div class ="center" > center</div > <div class ="right" > right</div > </div > </body > </html >
table 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > CSS实现三栏布局-table布局</title > <style type ="text/css" > * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { width: 100%; display: table; height: 100px; } div { display: table-cell; } .left { width: 100px; background: red; } .center { background: green; } .right { width: 100px; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box" > <div class ="left" > left</div > <div class ="center" > center</div > <div class ="right" > right</div > </div > </body > </html >
position 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > CSS实现三栏布局-定位布局</title > <style type ="text/css" > * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { position: relative; } div { height: 100px; position: absolute; } .left { left: 0px; width: 100px; background: red; } .center { left: 100px; right: 100px; background: green; } .right { right: 0px; width: 100px; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box" > <div class ="left" > left</div > <div class ="center" > center</div > <div class ="right" > right</div > </div > </body > </html >
grid 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > CSS实现三栏布局-grid布局</title > <style type ="text/css" > * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { display: grid; grid-template-columns: 100px 1fr 100px; } div { height: 100px; } .left { background: red; } .center { background: green; } .right { background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box" > <div class ="left" > left</div > <div class ="center" > center</div > <div class ="right" > right</div > </div > </body > </html >
css如何实现左边定宽,右边自适应? 非严格意义 float+calc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适-float+calc</title > <style > * { margin :0 ; padding:0; // 清除浏览器默认样式 } .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; border : 1px solid #000 ; } .left-box { float :left ; width: 200px; height: 100%; background: red; } .right-box { float: right; width: calc(100% - 200px); // 100%是指父元素宽度的100% 即 .box-wrapper的宽度 600px height: 100%; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
inline- block- calc 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适-inline-block+calc</title > <style > * { margin :0 ; padding :0 ; } .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; border : 1px solid #000 ; } .left-box { display: inline-block; width: 200px; height: 100%; background: red; } .right-box { display: inline-block; width: calc(100% - 200px); height: 100%; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
position+margin/padding 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适应 + position + margin</title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; position: relative; border : 1px solid #000 ; } .left-box { width: 200px; height: 100%; background: red; position: absolute; } .right-box { margin-left :200px ; // padding-left:200px; // 效果和margin-left:200px;一样 height: 100%; background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
严格意义 flex布局 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适 - flex </title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; border :1px solid #000 ; display: flex; } .left-box { width: 200px; height: 100%; background: red; } .right-box { background: blue; flex: 1; // 占满剩余的空间 } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
table布局 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适 - table 布局 </title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; border : 1px solid #000 ; display: table; } .left-box { width: 200px; height: 100%; background: red; display: table-cell; } .right-box { height: 100%; background: blue; display: table-cell; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
grid布局 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 左边定宽右边自适 + grid 布局</title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 600px; height: 400px; border :1px solid #000 ; display: grid; grid-template-columns: 200px auto; } .left-box { background: red; } .right-box { background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="left-box" > left-box </div > <div class ="right-box" > right-box </div > </div > </body > </html >
CSS如何实现绝对居中? 定宽高 绝对定位+负margin值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > css绝对居中- (定宽高) 绝对定位 + 负magin值</title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; } .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; position: absolute; left: 50%; top: 50%; margin-left: -50px; margin-top: -50px; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="box" > </div > </div > </body > </html >
绝对定位+ margin auto 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > css绝对居中- (定宽高) 绝对定位 + margin auto</title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; } .box { width: 100px; height: 100px; background: blue; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; right: 0; bottom: 0; margin: auto; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="box" > </div > </div > </body > </html >
不定宽高 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > css绝对居中- (不定宽高) 绝对定位 + transform</title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; position: relative; } .box { background: yellow; position: absolute; left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translate(-50%, -50%); } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="box" > 绝对定位+transform </div > </div > </body > </html >
table- cell 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > css绝对居中- (不定宽高) table-cell </title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle; text-align: center; } .box { background: yellow; display: inline-block; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="box" > table-cell </div > </div > </body > </html >
flex布局 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > css绝对居中- (不定宽高) flex布局 </title > <style > .box-wrapper { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid red; display: flex; justify-content: center; align-items: center; } .box { background: blue; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-wrapper" > <div class ="box" > flex布局 </div > </div > </body > </html >
清除浮动有哪些方法,各有什么优缺点? 为什么要清除浮动?
float导致子元素脱离文档流,父元素无法计算子元素高度
清除浮动有哪些方法?各有什么优缺点
父元素固定宽高
优点:简单,代码量少,没有兼容问题
缺点:内部元素高度不确定的情况下无法使用
添加新元素
优点:简单,代码量少,没有兼容问题
缺点:需要添加无语义的html元素,代码不够优雅,不便于后期的维护
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 清除浮动(2)添加新元素</title > <style > .box-container { width: 142px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid red; } img { width: 45px; height: 45px; float: left; margin-right: 10px; } .right-box { float: right; } .right-box-title { font-size: 16px; color : #1C1F21 ; } .right-box-content { font-size: 12px; color : #545C63 ; } .clear-element { clear: both; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-container" > <img src ="./image/java.jpg" alt ="javajpg" > <div class ="right-box" > <div class ="right-box-title" > java工程师</div > <div class ="right-box-content" > 综合就业率第一</div > </div > <div class ="clear-element" > </div > </div > </body > </html >
使用伪元素
优点:仅用css实现,不容易出现怪问题
缺点:仅支持IE8以上和非IE浏览器
触发父元素BFC
优点:仅用css实现,代码少,浏览器支持好
缺点:用overflow: hidden触发BFC的情况下,可能会使内部本应正常显示的元素被裁剪
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > 清除浮动(4)触发父元素BFC</title > <style > .box-container { width: 142px; border: 1px solid red; padding: 10px; overflow: auto; } img { width: 45px; height: 45px; float: left; margin-right: 10px; } .right-box { float: right; } .right-box-title { font-size: 16px; color : #1C1F21 ; } .right-box-content { font-size: 12px; color : #545C63 ; } .content { width: 400px; height: 300px; background : #000 ; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="box-container" > <img src ="./image/java.jpg" alt ="javajpg" > <div class ="right-box" > <div class ="right-box-title" > java工程师</div > <div class ="right-box-content" > 综合就业率第一</div > </div > </div > </body > </html >
如何用css画一个三角形? 用css画三角形的场景有哪些?
如何用css画一个三角形
利用了border四个方向相接的位置斜切的特性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > Document</title > <style > .triangle { width :0 ; border-top: 10px solid transparent; border-right: 10px solid transparent; border-bottom: 10px solid blue; border-left: 10px solid transparent; } </style > </head > <body > <div class ="triangle" > </div > </body > </html >
为什么要用css画三角形的原因 出于页面性能考虑,避免发送过多的http请求,节省带宽
css提高页面性能的方法 1.属性设置使用简写,目的:减小生产包体积.
二、javascript 面试题 介绍下原型和原型链
么是原型和原型链?
什么是原型
在 javascript 中,函数可以有属性。每个函数都有一个特殊的属性叫作原型(prototype)
什么是原型链
原型链就是当我们访问对象的某个属性或方法时,如果在当前对象中找不到定义,会继续在当前对象的原型对象中查找,如果原型对象中依然没有找到,会继续在原型对象的原型中查找(原型也是 对象,也有它自己的原型)如此继续,直到找到为止,或者查找到最顶层的原型对象中也没有找到,就结束查找,返回 undefined。可以看出,这个查找过程是一个链式的查找,每个对象都有一个到它自身原型对象的链接,这些链接组件的整个链条就是原型链
原型和原型链存在的意义是什么?
使得实例对象可以共享构造函数原型属性和方法, 节省内存。构造函数原型上的属性和方法越多,节省内存越大.
如何理解作用域和作用域链?
什么是作用域?
作用域是在运行时代码中的某些特定部分中变量,函数和对象的可访问性,作用域决定了代码区块中变量和其他资源的可见性。
作用域分为:全局作用域、局部作用域(函数作用域)、块级作用域(if、for)
作用域存在的意义是什么?
作用域存在的最大意义就是变量隔离,即:不同作用域下同名变量不会有冲突。
什么是作用域链?
当我们在某个函数的内部作用域中查找某个变量时, 如果没有找到就会到他的父级作用域中查找, 如果父级也没找到就会接着一层一层的向上寻找,直到找到全局作用域还是没找到的话,就宣布放 弃。这种一层一层的作用域嵌套关系,就是作用域链。
介绍下闭包
什么是闭包?
大白话:能够访问其他函数内部变量的函数,被称为闭包。
闭包有哪些实际的使用场景?
a、事件函数的封装 b、用闭包模拟私有方法 c、在循环中给页面元素绑定事件响应函数 d、防抖函数和节流函数的timer e、Object.defineProperty实现响应式
闭包存在什么问题?
闭包本身会造成内部变量常驻内存
闭包跟内存泄漏有关的地方是,使用闭包的同时比较容易循环引用,如果闭包的作用域中保存着一些 DOM 节 点,这时候可能会造成内存泄漏,但从本质上来讲这并给闭包的问题,在 IE浏览器中由于 BOM 的 DOM 中的对象是使用 c++以 COM 对象方式实现的, 而 COM 的垃圾回收机制使用的是引用计数策略, 也就是说如果两个对象之间形成的循环引用,那么这两个对象都无法被回收,从本质上来讲这并非闭包的锅
bind&call&apply的区别?
相同点
bind,call, apply都可 以改变this指向
不同点
1 call和apply的传参方式不同
2 bind和call, apply的返回值不同
bind,call,apply的使用场景
call
判断数据类型
类数组转数组
Object.defineProperty实现响应式,处理数组的方法时使用
apply
bind
多种方式实现数组去重? 普通数组去重 filter+indexOf
利用了indexOf返回的是查到第一个元素的下标,而遍历到后续重复的元素时,元素下标一定与第一个元素的下标不同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 const unique = (arr ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } return arr.filter((item, index ) => { return arr.indexOf(item) === index }) }
sort+相邻判断 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const unique = (arr ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } arr = arr.sort() let res = [] for (let i = 0 ; i<arr.length; ++i){ if (arr[i] !== arr[i-1 ]){ res.push(arr[i]) } } return res }
set+解构赋值 1 2 3 4 5 6 const unique = (arr ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } return [...new Set (arr)] }
set与Array.from 1 2 3 4 5 6 const unique = (arr ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } return Array .from(new Set (arr)) }
对象数组去重 临时对象缓存数组项key值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 const unique = (arr, key ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } let hasKeyValue = {} let res = [] for (let i = 0 ; i < arr.length; ++i){ let keyValue = arr[i][key] if (!hasKeyValue[keyValue]){ res.push(arr[i]) hasKeyValue[keyValue] = true } } return res }
reduce方法+缓存对象 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const unique = (arr, key ) => { if (!Array .isArray(array)){ throw new Error ("unique function params is not Array" ) } let hasKeyValue = {} return arr.reduce((pre, cur ) => { hasKeyValue[cur[key]] ? "" : hasKeyValue[cur[key]] = true && pre.push(cur) return pre }, []) }
给定数组求最大值?
1 2 const res = Math .max(...array)const res = Math .max.apply(null ,array)
1 2 3 4 5 function getMax (array ) return array.reduce((prev,current )=> { return current>prev?current:prev }) }
1 2 3 4 function getMax (array ) const result = array.sort(); return result[result.length-1 ]; }
js中判断类型的方式有哪些? js中判断数据类型的场景?
js中有哪些数据类型?
基本数据类型:
String、Number、Boolean、Symbol、undefined、Null
引用数据类型:
Object、Array、Function、 Date、FormData、Set、Map等等
js中判断类型的方式有哪些?
实现函数防抖
实现函数节流
多种方式实现数组拍平
将多维数组变成一维数组
reduce+concat
利用concat可以将一个元素和一个数组拼接成一个数组
1 2 3 4 5 const flatten = (arr ) => { return arr.reduce((pre, cur ) => { return pre.concat(Array .isArray(cur) ? flatten(cur) : cur) },[]) }
es6自带的flat函数 1 2 3 const flatten = (arr ) => { return arr.flat(Infinity ) }
while+...+concat+some
利用concat可以将一个元素和一个数组拼接成一个数组
some执行数组每个元素,如有满足添加的则返回true,后续元素不再执行,若没有满足条件的元素则返回false
1 2 3 4 5 6 const flatten = (arr ) => { while (arr.some(Array .isArray)){ arr = [].concat(...arr) } return arr }
使如下判断成立
Object.defineProperty实现对数据的监听
实现vue2中的响应式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <meta http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" content ="IE=edge" > <meta name ="viewport" content ="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" > <title > question</title > </head > <body > <script > let value = 0 ; Object .defineProperty(window ,'a' ,{ get (){ return value += 1 ; } }); if(a===1&&a===2&&a===3){ console .log(`object` ) } </script > </body > </html >
如何实现new操作符
new
实例化对象:把一个构造函数变成一个对象
返回值的问题: 构造函数中如果有值返回 那实例化后的对象就是这个返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 const TMap = function (options ) this .name = options.name; this .address = options.address; } const ObjectFactory = (...args )=> { const obj = {}; const Constructor = args.shift() obj.__proto__ = Constructor.prototype; const ret = Constructor.apply(obj,args); return typeof ret === 'object' ? ret: obj; } const map = ObjectFactory(TMap,{name :"MAP" ,address :"BJ" }); console .log('map :>> ' , map);
如何实现一个bind函数
核心点
bind函数改变this指向
bind函数是Function. prototype上的方法
bind函数的返回值也是函数
bind函数调用之后返回的函数的参数同样也接收处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 Function .prototype.bind1 = function ( const args = Array .prototype.slice.call(arguments ) const t = args.shift() const self = this return function ( const returnArgs = Array .prototype.slice.call(arguments ) return self.apply(t, args.concat(returnArgs)) } } function fn1 (a, b, c ) console .log('this' , this ) console .log(a, b, c) return 'this is fn1' } const fn2 = fn1.bind1({x : 100 }, 10 , 20 )const res = fn2(30 ) console .log(res)this { x : 100 }10 20 30 this is fn1
如何实现call&apply函数
核心点
call
改变thi s指针
返回函数调用
参数挨个依次传递
apply
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 const obj = { name: "freemen" } function testFunc (a,b ) console .log('a :>> ' , a); console .log('b :>> ' , b); console .log('this.name :>> ' , this .name); } const core = (context,args,_this ) => { args = args || []; const key = Symbol (); context[key] = _this; const result = context[key](...args) delete context[key] return result; } Function .prototype.callFn = function (context,...args ) return core(context,args,this ); } Function .prototype.applyFn = function (context,args ) return core(context,args,this ); } testFunc.callFn(obj,'a' ,'b' ); testFunc.applyFn(obj,['a' ,'b' ]);
如何实现instanceof 三、ES6 面试题 let const和var的区别
var 和let是变量,可修改;const是常量,不可修改;
let const 有块级作用域,var没有
var是 ES5语法,let const是ES6语法;var有变量提升
let定义变量会有暂时性死区,即不能在定义前给变量赋值
let、const定义的变量不会挂载在window上,但是var会
const使用注意事项
定义之后不能修改
在定义时 必须附初始值
定义的对象不能修改 但是对象内的属性可以修改
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 console .log(a) var a = 200 var aconsole .log(a) a = 200 var fullName = 'freemen' ;function f ( console .log(`fullName` , fullName) if (false ){ var fullName = "mkw" } } f() console .log(b)let b = 100 var fullName = "freemen" ;if (true ){ fullName = 'test' let fullName; } <script> var fullName ='freemen' ; console .log(`window` , window .fullName) let fullName ='freemen' ; console .log(`window` , window .fullName) </script>
箭头函数和普通函数的区别
箭头函数的this指向父级作用域的this
.call()、 .apply()、 .bind()无法改变箭头函数中this的指向
不会报错,但函数类使用的变量可能是undefined
本质还是因为箭头函数的this指向父级作用域的this,不会指向指定的对象,而是指向指定对象的父级作用域的this
不可以被当作构造函数
不可以使用arguments对象
箭头函数使用arguments对象会直接报错,提示没有定义
通过...args的方式接收参数,且args就是数组,不是类数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function test ( console .log(arguments ) } test('a' , 'b' , 100 ) const test1 = (...args ) => { console .log(args) } test1('a' , 'b' , 100 ) const test2 = (args ) => { console .log(args) } test2('a' , 'b' , 100 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const res = sum(10 , 20 )console .log(res) function sum (x, y ) return x + y } var res = sum(10 , 20 )console .log(res) var sum = function (x, y ) return x + y }
箭头函数不支持new.target
直接报错
new.target返回一个指向构造方法或函数的引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function Person ( this .name = 'chuckie' const target = new .target console .log(target) } const obj = new Personconst Person1 = () => this .name = 'chuckie' const target = new .target console .log(target) } const obj1 = new Person1
forEach、for in、for of三者的区别
forEach是数组的方法 同步执行
便利的时候更加简洁,效率和 for 循环相同,不用关心集合下标的问题,减少了出错的概率。
没有返回值
不能使用 break 中断循环,不能使用 return返回到外层函数
for…in用于循环遍历数组或对象属性(大部分用于对象, 遍历键值) 同步执行
for…of一个数据结构只要部署了 Symbol.iterator 属性,就被视为具有 iterator 接口,就可以用 for…of循环遍历它的成员,可用 for…of遍历的成员包括:数组, Set 和 Map 结构, 类数组对象 异步执行
ES6中数组去重方法
ES6中对象新增的方法有哪些?
Object.is()
用来比较两个值是否严格相等,与(===)基本类似,可以判断值类型也可以判断对象(判断引用是否相等),也可以判断特殊数据NaN
有===为什么还要有Object.is() , ===不能判断NaN === NaN,但是Object.is()可以
1 2 3 4 5 if (NaN ===NaN ){ console .log(`getName` ); } const result = Object .is(NaN ,NaN );console .log(`result` , result);
Object.assign()
Object.keys()
返回一个数组,成员是参数对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可遍历( enumerable )属性的键名
Object.values()
返回一个数组,成员是参数对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可遍历( enumerable )属性的键值
Object.entries ()
返回一个二维数组,成员是参数对象自身的(不含继承的)所有可遍历( enumerable )属性的键值对数组
数组的第一维是键名数组
数组的第二维是键值数组
class 和 function 的区别
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Persion constructor (){ this .fullName = "freemen" ; } } const obj = { fullName: "freemen" } sayName.call(obj) Persion.call(obj)
Promise
Promise.prototype.then
可以支持链式调用
then 接受两个参数且都是函数
返回值也是Promise(新的)
Promise.prototype.catch() 捕获Promise错误
Promise.prototype.finally()
用于指定不管 Promise 对象最后状态如何,都会执行的操作
Promise.all
Promise.race
Promise.resolve 返回一个Promise实例 -> resolved
Promise.reject 返回一个Promise实例 -> rejected
...的实现原理1 2 3 const arr = [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ]const arr1 = [...arr]const arr2 = [].concat(arr)
四、HTTP 面试题 网络分层模型 常见的状态码 http有哪些请求方法? GET和POST有什么区别?
get用来获取数据,post用来提交数据
get参数有长度限制(受限于url长度,具体的数值取决于浏览器和服务器的限制,最长2048字节) , 而post无限制。
get是明文传输, post是放在请求体中
Get具有数据缓存,而Post没有
accept:代表客户端希望接受的数据类型
accept-encoding:浏览器发给服务器,声明浏览器支持的编码类型
accept-language:表示浏览器所支持的语言类型
Cache-Control:缓存开关,no- -cache表示禁用缓存
referer: referer的正确英语拼法是referrer。由于早期HTTP规范的拼写错误,主要用于防止盗链和恶意请求
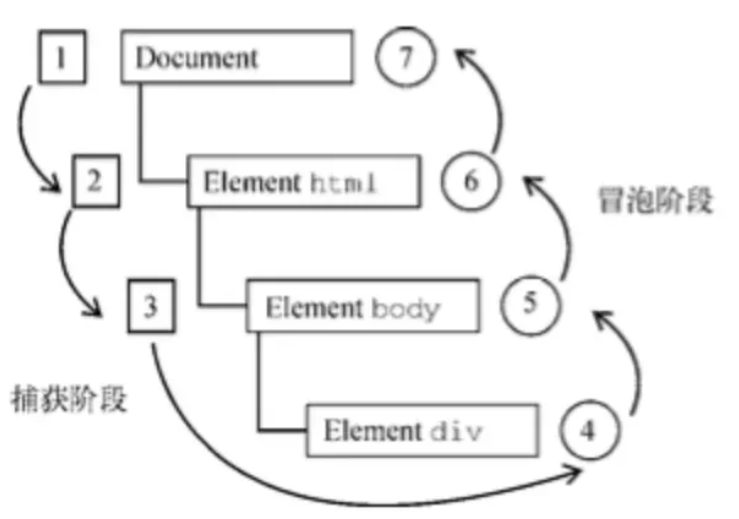
五、浏览器 面试题 浏览器的事件传输机制原理
背景:
事件传输机制冒泡和捕获分别由微软和网景公司提出
这两个概念都是为了解决页面中事件流(事件发生顺序)的问题
事件触发的三个阶段
localStorage和sessionStorage的区别
相同点
不同点
localStorage 数据会永久存储,除非代码或手动删除 ,(多用此方法)
sessionStorage数据只存在于当前会话,浏览器关闭则清空
浏览器的事件循环机制
Javascript(0x06)-js异步中的任务队列
宏任务和微任务
宏任务
script块(最开始的代码块)
定时器
ajax网络请求
dom事件
微任务
浏览器的回流和重绘 浏览器的渲染过程
解析HTML,生成DOM树,解析CSS,生成CSSOM树
将DOM树和CSSOM树结合,生成渲染树(Render Tree)
Layout(回流):根据生成的渲染树,进行回流(Layout),得到节点的几何信息(位置,大小)
Painting(重绘):根据渲染树以及回流得到的几何信息,得到节点的绝对像素
调用GPU触发渲染,将结果展示在页面上
回流和重绘的概念
回流: 通过构造渲染树,将可见DOM节点以及它对应的样式结合起来,可是还需要计算其在设备视口(viewport)内的确切位置和大小,这个计算的阶段就是回流
重绘:通过构造渲染树,知道了哪些节点是可见的,以及可见节点的样式和具体的几何信息(位置、大小) ,那么就可以将渲染树的每个节点都转换为屏幕上的实际像素,这个阶段就叫做重绘节点
软件工程和建筑学的渊源
回流:相当于把房子拆了重建
重绘:相当于重新粉刷
结论:回流必然导致重绘, 重绘不一 定会伴随着回流
何时触发回流和重绘
添加或删除可见的DOM元素
元素的内容、位置或尺寸发生变化
页面一开始渲染的时候
浏览器的窗口尺寸变化
如何避免回流和重绘
使用文档片段fragment,将多次修改合并为一次
跨域问题
HTTP(0x03)-跨域问题
同源策略
什么是跨域
跨域的常见解决方案
jsonp
原理:利用<script>标签没有跨域限制的漏洞,网页可以得到从其他来源动态产生的JSON数据。JSONP请求一定需要对方的服务 器做支持才可以。(https://www.imooc.com?callback getData)
优点: 简单兼容性好,可用于解决主流浏览器的跨域数据访问的问题
缺点:仅支持get方法具有局限性不安全可能会遭受XSS攻击
CORS
postMessage
postMessage是HTML5 XMLHttpRequest Level 2中的API,且是为数不多可以跨域操作的window属性之一 , 它可用于解决以下方面的问题
页面和其打开的新窗C的数据传递
多窗口之间消息传递
页面与嵌套的iframe消息传递
上面三个场景的跨域数据传递
nginx反向代理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 server { listen 80 ; server_name wwW.imooc.com; location / { proxy_pass http: } }
浏览器的主要组成部分
用户界面:包括地址栏、前进/后退按钮、书签菜单等。除了浏览器主窗口显示的请求的页面外,其他显示的各个部分都属于用户界面。
浏览器引擎:在用户界面和呈现引擎之间传送指令。
渲染引擎:负责显示请求的内容。如果请求的内容是HTML,它就负责解析HTML和CSS内容,并将解析后的内容显示在屏幕上
网络模块:用于网络调用,比如HTTP请求。其接口与平台无关并为所有平台提供底层实现。
用户界面后端:用于绘制基本的窗口小部件,比如组合框和窗口。其公开了与平台无关的通用接口,而在底层使用操作系统的用户界面方法。
JavaScript解释器:用于解析和执行JavaScript代码。
数据存储模块:这是持久层。浏览器需要在硬盘上保存各种数据.例如Cookie SessionStorage LocalStorage
从输入一个URL到页面展示整个过程中发生了什么
11-6.pdf
首先讲清楚主流程:
其一是网页加载过程,就是从 URL到构建DOM树
其二就是网页渲染过程,从DOM生成可视化图像
其次讲清楚渲染过程中包含的数据和模块
数据: 网页内容,DOM, 内部表示和图像
模块则包括: HTML 解释器,css 解释器,javascript引擎,布局和绘图模块
最后讲清楚页面渲染的三个阶段以及具体的步骤:
第一个阶段就是从网页的URL到构建完DOM树
第二个阶段是从DOM树到构建完WebKit的绘图上下文
第三个阶段是从绘图上下文生成最终的图像
六、Vue 面试题 生命周期
beforeCreate
created
beforeMount
mounted
beforeUpdate.
updated
beforeDestroyed
destroyed
父子组件生命周期执行顺序 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 父组件-beforeCreate 父组件-created 父组件-beforeMount 子组件-beforeCreate 子组件-created 子组件-beforeMount 子组件-mounted 父组件-mounted 父组件 beforeUpdate 子组件 beforeUpdate 子组件 updated 父组件 updated 父组件 beforeDestroy 子组件 beforeDestroy 子组件 destroyed 父组件 destroyed
keep-alive
keep-alive官网
与动态组件组合使用
核心点是缓存组件,保存组件中的状态
缓存实例的生命周期
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 export default { activated() { }, deactivated() { } }
哪个生命周期函数中进行网络请求
created、beforeMount、mounted都可
选择created (created阶段data,methods已经完成初始化)
能更快获取到服务端数据,减少页面 loading 时间;
ssr (服务端渲染)不支持 beforeMount 、mounted 钩子函数,所以放在 created 中有助于一致性;
选择mounted (页面已经渲染完成)
如果需要获取dom信息再请求,则需要在这个阶段
会触发dom的二次渲染,容易造成页面闪屏问题
v-if vs v-show